I study the physiological tactics bacteria have evolved to cope with fluctuations in resource availability.
1) Are microbial growth laws developed in the lab useful for understanding how single-cells grow in nature?
Bacteria are small when starving for nutrients, and get bigger when nutrients appear. However, the amount of mass cells accumulate before dividing depends on the quality of the nutrients they eat. We are trying to understand if the dynamics of mass accumulation for bacteria growing in natural ecosystems are similar to what we know from steady-state growth in the lab. We are also examining the ecological consequences of the divergent mass accumulation tactics of different bacteria.
See our recent publication in mbio.
2) What are the costs and benefits of storage compound metabolism for individual bacterial cells and populations?
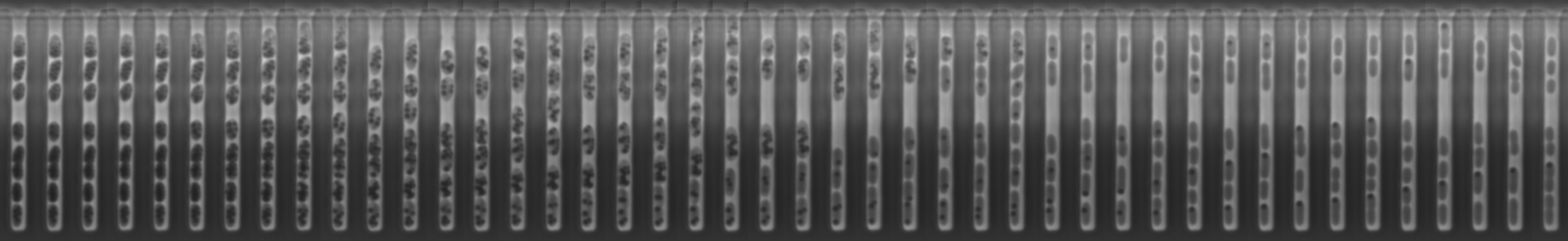
Bacteria can stockpile excess nutrients as intracellular storage compounds. The costs and benefits of storage compound metabolism are complex, depending on an organism’s physiology as well as its ecological context. While individual cells bear the costs and reap the benefits of storage compound metabolism, cell-to-cell variation in a population can lead to complex ecological and evolutionary dynamics. I am using the model organism Vibrio natriegens to examine how storage compound metabolism during nutrient fluctuations influences the ability of individual cells to grow when nutrients return to steady-state. With a combination of experiments at the level of individual cells (using microfluidic cultivation) and populations (using batch cultivation), I am examining how physiology, ecology, and evolution interact to shape the costs and benefits of storage compound metabolism.
3) Does rRNA operon (rrn) copy number reflect adaptation to resource availability?
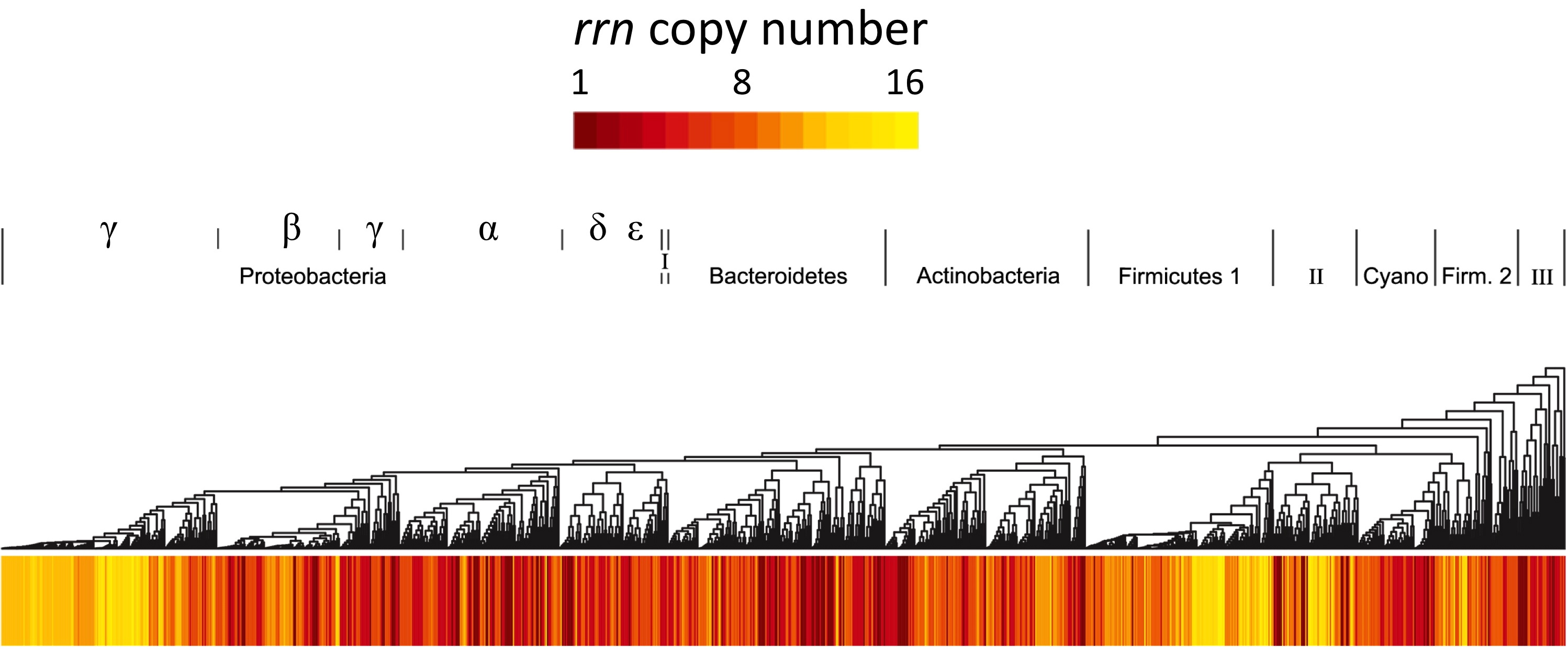
Resource availability is a strong force driving bacterial evolution. Growth rate and growth efficiency are complex traits that influence fitness and they are favored under contrasting resource regimes.
Fast growing bacteria require a high cellular ribosome content and often possess many copies of the ribosomal RNA operon (rrn) in their genome. However, some of the most numerically dominant bacteria on Earth grow relatively slowly and possess few rrn copies (e.g. the Pelagibacterales in the ocean and the Acidobacteria in soils).
Across many species I have found that rrn copy number can explain variation in a species growth rate and efficiency. Traits associated with resource preference (e.g. genome streamlining, chemotaxis) also have the expected relationship with rrn copy number, indicating it is a good predictor of resource adaptation.
Below is a talk I gave on this research in 2015 for the micro seminar.